Manufacturing Industry Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Production
Related Articles: Manufacturing Industry Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Production
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Manufacturing Industry Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Production. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Manufacturing Industry Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Production
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Manufacturing Industry Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Production
- 3.1 1. The Rise of Digital Transformation
- 3.2 2. Focus on Sustainability and Circular Economy
- 3.3 3. The Rise of Automation and Robotics
- 3.4 4. The Importance of Skilled Labor and Workforce Development
- 3.5 5. The Growing Importance of Supply Chain Resilience
- 3.6 6. The Rise of Personalized and Customized Manufacturing
- 3.7 7. The Growing Role of Data and Analytics
- 3.8 8. The Importance of Collaboration and Partnerships
- 3.9 Related Searches
- 3.10 FAQs
- 3.11 Tips
- 3.12 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Manufacturing Industry Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Production

The manufacturing industry is undergoing a period of rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer demands, and a global shift towards sustainability. As we approach 2025, several key trends will continue to shape the landscape of manufacturing, presenting both challenges and opportunities for businesses.
This comprehensive exploration delves into the critical manufacturing industry trends 2025, examining their impact on the industry and providing insights into how manufacturers can adapt and thrive in this evolving environment.
1. The Rise of Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is no longer a buzzword; it’s a necessity for manufacturers seeking to remain competitive. This trend encompasses the integration of digital technologies across all aspects of the manufacturing process, from design and engineering to production, supply chain management, and customer service.
Key elements of digital transformation in manufacturing include:
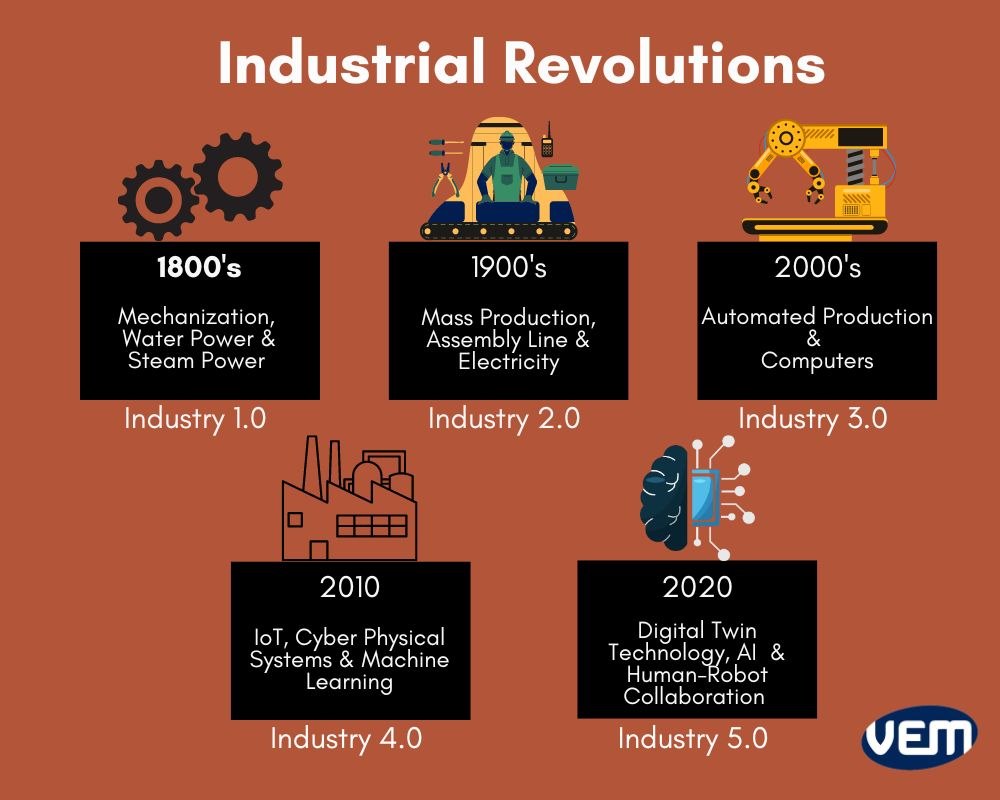
- Industry 4.0 Technologies: The adoption of technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and advanced robotics is revolutionizing manufacturing processes. AI-powered systems can optimize production lines, predict maintenance needs, and improve quality control. IoT sensors gather real-time data from machines and equipment, enabling better decision-making and predictive maintenance. Cloud computing provides scalable and secure data storage and processing capabilities, allowing manufacturers to access and analyze data from anywhere.
- Digital Twins: Digital twins are virtual representations of physical assets, such as machines, products, or entire factories. They enable manufacturers to simulate and test various scenarios, optimize performance, and identify potential problems before they occur.
- Advanced Analytics: The ability to collect, analyze, and interpret vast amounts of data is critical for manufacturers. Advanced analytics can help identify trends, predict demand, optimize resource allocation, and improve decision-making.
- Cybersecurity: As manufacturing systems become increasingly interconnected, cybersecurity becomes paramount. Protecting sensitive data and ensuring the integrity of manufacturing processes is crucial to prevent disruptions and data breaches.
Benefits of Digital Transformation:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Digital technologies streamline processes, automate tasks, and optimize resource allocation, leading to significant increases in efficiency and productivity.
- Enhanced Quality and Consistency: Digital tools enable better quality control, reduce defects, and ensure consistent product quality.
- Improved Decision-Making: Real-time data and advanced analytics provide valuable insights that empower manufacturers to make better informed decisions.
- Greater Flexibility and Agility: Digital technologies enable manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing market conditions and customer demands.
2. Focus on Sustainability and Circular Economy
Sustainability is no longer a niche concern; it’s a core business imperative for manufacturers. Consumers are increasingly demanding environmentally friendly products, and regulatory pressures are mounting.
Key aspects of sustainability in manufacturing:
- Reducing Environmental Impact: Manufacturers are adopting sustainable practices to minimize their carbon footprint, reduce waste, and conserve resources. This includes using renewable energy sources, implementing energy-efficient processes, and minimizing the use of hazardous materials.
- Circular Economy Principles: The circular economy promotes the reuse and recycling of materials, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact. Manufacturers are exploring ways to incorporate circular economy principles into their operations, such as designing products for disassembly, using recycled materials, and extending product lifecycles.
- Sustainable Supply Chains: Manufacturers are working with their suppliers to ensure ethical and sustainable sourcing practices. This includes verifying the origin of materials, promoting fair labor practices, and reducing the environmental impact of transportation.
Benefits of Sustainability:
- Improved Brand Image and Reputation: Consumers are increasingly attracted to brands that prioritize sustainability.
- Reduced Costs: Sustainable practices can lead to cost savings through energy efficiency, waste reduction, and optimized resource utilization.
- Enhanced Competitiveness: Sustainability is becoming a key differentiator in the market, giving manufacturers a competitive edge.
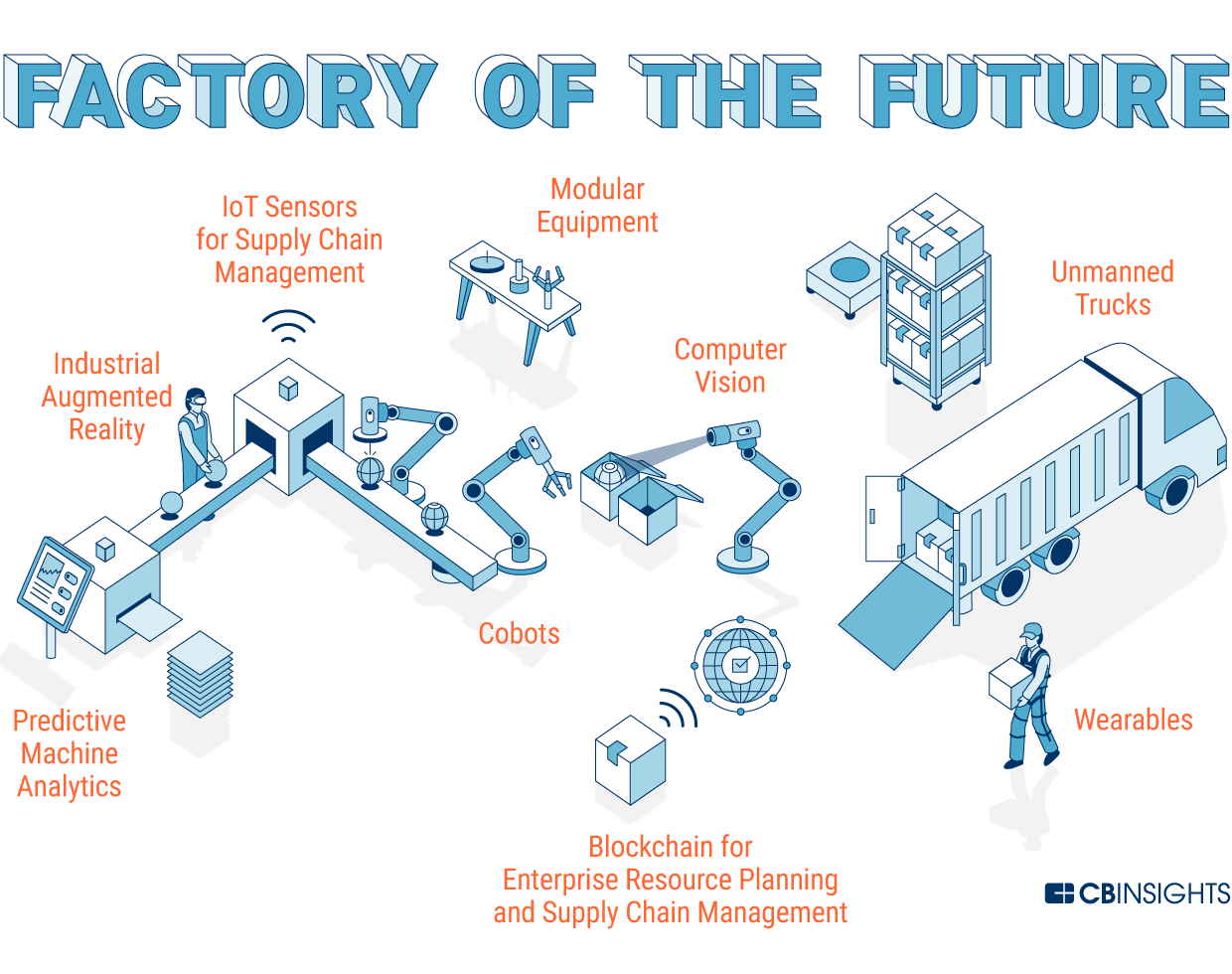
3. The Rise of Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics are playing an increasingly significant role in manufacturing, transforming production processes and enhancing efficiency.
Key aspects of automation and robotics:
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Cobots are designed to work alongside human workers, assisting with tasks that are repetitive, dangerous, or physically demanding. They can enhance productivity, improve safety, and free up human workers to focus on more complex tasks.
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): AGVs are autonomous vehicles that transport materials within a factory, reducing the need for manual handling and improving efficiency.
- Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS): AS/RS are automated systems that manage and retrieve materials from storage, optimizing space utilization and improving inventory management.
- 3D Printing: 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is revolutionizing the way products are designed and manufactured. It allows manufacturers to create complex shapes and geometries, customize products, and reduce lead times.
Benefits of Automation and Robotics:
- Increased Productivity: Automation and robotics can significantly increase production output and reduce labor costs.
- Improved Accuracy and Consistency: Automated systems are typically more accurate and consistent than human workers, leading to fewer defects and improved product quality.
- Enhanced Safety: Robots can perform dangerous or hazardous tasks, reducing the risk of workplace injuries.
- Greater Flexibility and Customization: Automation allows manufacturers to quickly adapt to changing production needs and customer demands.
4. The Importance of Skilled Labor and Workforce Development
The rapid pace of technological change in manufacturing is creating a demand for skilled workers with specialized knowledge and abilities.
Key aspects of workforce development:
- Upskilling and Reskilling: Manufacturers are investing in training programs to upskill their existing workforce and reskill workers for new roles in the evolving manufacturing landscape.
- STEM Education: Encouraging STEM education (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) is crucial to developing a pipeline of skilled talent for the manufacturing industry.
- Attracting and Retaining Talent: Manufacturers need to create attractive working environments that offer competitive salaries, benefits, and career development opportunities to attract and retain skilled workers.
Benefits of Skilled Labor:
- Improved Productivity and Innovation: A skilled workforce is essential for driving productivity, efficiency, and innovation in manufacturing.
- Reduced Errors and Defects: Skilled workers are better equipped to identify and address potential problems, reducing errors and defects in production.
- Enhanced Safety: Well-trained workers are more aware of safety hazards and protocols, leading to a safer working environment.
5. The Growing Importance of Supply Chain Resilience
Global supply chains have become increasingly complex and interconnected, making them vulnerable to disruptions.
Key aspects of supply chain resilience:
- Diversification of Suppliers: Manufacturers are diversifying their supply chains to reduce their reliance on any single supplier, minimizing the impact of disruptions.
- Nearshoring and Reshoring: Some manufacturers are bringing production closer to their customers or relocating manufacturing facilities back to their home countries to reduce transportation costs, lead times, and supply chain risks.
- Advanced Supply Chain Management Technologies: Manufacturers are adopting technologies like blockchain, AI, and IoT to improve supply chain visibility, track inventory, and optimize logistics.
Benefits of Supply Chain Resilience:
- Reduced Risk of Disruptions: A resilient supply chain can withstand disruptions caused by factors such as natural disasters, political instability, or global pandemics.
- Improved Inventory Management: Advanced technologies can help optimize inventory levels, reducing storage costs and minimizing the risk of stockouts.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: A resilient supply chain ensures timely delivery of products, improving customer satisfaction.
6. The Rise of Personalized and Customized Manufacturing
Consumers are increasingly demanding personalized and customized products, creating new opportunities for manufacturers.
Key aspects of personalized manufacturing:
- Mass Customization: Manufacturers are using digital technologies to enable mass customization, offering a wide range of product options and allowing customers to personalize their purchases.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): 3D printing allows manufacturers to produce highly customized products on demand, reducing lead times and enabling the creation of complex geometries.
- Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Models: Manufacturers are increasingly selling directly to consumers, bypassing traditional retail channels and building closer relationships with customers.
Benefits of Personalized Manufacturing:
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Personalized products meet individual needs and preferences, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
- Enhanced Brand Loyalty: Personalized experiences foster stronger customer relationships and encourage brand loyalty.
- New Revenue Streams: Personalized products can command premium prices, creating new revenue streams for manufacturers.
7. The Growing Role of Data and Analytics
Data is becoming a valuable asset for manufacturers, providing insights into customer behavior, market trends, and production processes.
Key aspects of data and analytics in manufacturing:
- Data Collection and Integration: Manufacturers are collecting data from various sources, including sensors, machines, and customer interactions, and integrating it into a central platform.
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics uses historical data to identify patterns and predict future outcomes, enabling manufacturers to anticipate demand, optimize production, and prevent potential problems.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Data and analytics provide insights that empower manufacturers to make more informed decisions about everything from product design to marketing strategies.
Benefits of Data and Analytics:
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: Data-driven insights can optimize production processes, reduce waste, and improve resource allocation.
- Enhanced Quality Control: Data can help identify potential defects and improve quality control measures.
- Increased Profitability: By optimizing operations and making better decisions, manufacturers can increase profitability.
8. The Importance of Collaboration and Partnerships
Collaboration and partnerships are becoming increasingly important for manufacturers to access new technologies, expertise, and resources.
Key aspects of collaboration and partnerships:
- Open Innovation: Manufacturers are embracing open innovation models, collaborating with universities, research institutions, and other companies to develop new technologies and solutions.
- Industry Consortia: Manufacturers are joining industry consortia to share best practices, develop industry standards, and collaborate on research and development initiatives.
- Strategic Alliances: Manufacturers are forming strategic alliances with suppliers, distributors, and technology providers to gain access to complementary resources and capabilities.
Benefits of Collaboration and Partnerships:
- Access to New Technologies and Expertise: Collaborations enable manufacturers to tap into external expertise and technologies that they might not have internally.
- Reduced Costs and Risk: Sharing resources and expertise can reduce costs and risks for manufacturers.
- Enhanced Innovation: Collaboration fosters innovation by bringing together diverse perspectives and ideas.
Related Searches
Here are some related searches that provide additional insights into the manufacturing industry trends 2025:
- Future of Manufacturing: This broad search explores the long-term trends shaping the manufacturing industry, including automation, digitalization, and sustainability.
- Smart Factories: This search focuses on the concept of smart factories, which use digital technologies to optimize production processes and improve efficiency.
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): This search delves into the role of IoT in manufacturing, including how it is used to collect data, monitor equipment, and improve decision-making.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): This search explores the growing use of 3D printing in manufacturing, including its benefits and applications.
- Supply Chain Management Trends: This search examines the latest trends in supply chain management, including the importance of resilience, automation, and data analytics.
- Sustainability in Manufacturing: This search focuses on the growing importance of sustainability in manufacturing, including the adoption of circular economy principles and the reduction of environmental impact.
- Workforce Development in Manufacturing: This search explores the challenges and opportunities associated with workforce development in manufacturing, including the need for upskilling and reskilling.
- Manufacturing Industry 4.0: This search explores the impact of Industry 4.0 technologies on the manufacturing industry, including automation, digitalization, and data analytics.
FAQs
Q: What are the biggest challenges facing the manufacturing industry in 2025?
A: The manufacturing industry faces a number of challenges in 2025, including:
- The need to adopt new technologies: Manufacturers need to invest in digital technologies, automation, and robotics to remain competitive.
- The shortage of skilled labor: The industry is facing a shortage of skilled workers, particularly in areas like STEM and advanced manufacturing.
- The increasing complexity of global supply chains: Global supply chains are becoming more complex and vulnerable to disruptions.
- The pressure to be sustainable: Manufacturers are facing increasing pressure to reduce their environmental impact and adopt sustainable practices.
Q: What are the key opportunities for manufacturers in 2025?
A: Manufacturers have a number of opportunities to thrive in 2025, including:
- The growth of the digital economy: The digital economy is creating new opportunities for manufacturers to sell products and services online.
- The increasing demand for personalized products: Consumers are demanding more personalized products, creating opportunities for manufacturers to offer customized solutions.
- The growing importance of sustainability: Sustainability is becoming a key differentiator in the market, giving manufacturers a competitive edge.
- The rise of emerging markets: Emerging markets are offering new growth opportunities for manufacturers.
Q: How can manufacturers prepare for the trends shaping the industry in 2025?
A: Manufacturers can prepare for the trends shaping the industry in 2025 by:
- Investing in digital transformation: Manufacturers need to invest in digital technologies to improve efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness.
- Developing a skilled workforce: Manufacturers need to invest in training programs to upskill their existing workforce and attract new talent.
- Embracing sustainability: Manufacturers need to adopt sustainable practices to reduce their environmental impact and meet the demands of consumers.
- Building resilient supply chains: Manufacturers need to diversify their supply chains and adopt advanced supply chain management technologies to mitigate risks.
- Focusing on innovation: Manufacturers need to invest in research and development to create new products and processes.
- Collaborating with partners: Manufacturers can benefit from collaborating with universities, research institutions, and other companies to access new technologies and expertise.
Tips
Here are some tips for manufacturers to navigate the manufacturing industry trends 2025:
- Develop a clear digital transformation strategy: Define your digital transformation goals and develop a roadmap for achieving them.
- Invest in workforce development: Offer training programs to upskill your existing workforce and recruit new talent with the skills you need.
- Embrace sustainability: Set ambitious sustainability goals and develop a plan for achieving them.
- Build a resilient supply chain: Diversify your suppliers and implement advanced supply chain management technologies.
- Focus on innovation: Invest in research and development to create new products and processes.
- Collaborate with partners: Seek out opportunities to collaborate with universities, research institutions, and other companies.
- Stay informed about industry trends: Stay up-to-date on the latest trends and technologies shaping the manufacturing industry.
Conclusion
The manufacturing industry trends 2025 are shaping the future of production, creating both challenges and opportunities for manufacturers. By embracing digital transformation, prioritizing sustainability, investing in workforce development, and fostering innovation, manufacturers can navigate these trends and position themselves for success in the years to come. The ability to adapt, innovate, and collaborate will be critical for manufacturers seeking to thrive in this evolving landscape.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Manufacturing Industry Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Production. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
