Secular Trends in Epidemiology 2025: Shaping the Future of Public Health
Related Articles: Secular Trends in Epidemiology 2025: Shaping the Future of Public Health
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Secular Trends in Epidemiology 2025: Shaping the Future of Public Health. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Secular Trends in Epidemiology 2025: Shaping the Future of Public Health

The field of epidemiology, the study of the distribution and determinants of health and disease in populations, is constantly evolving. Secular trends in epidemiology refer to long-term, gradual changes in disease patterns over time, often driven by societal, environmental, and technological advancements. These trends are crucial for understanding the changing health landscape and developing effective public health interventions.
This exploration delves into the anticipated secular trends in epidemiology by 2025, examining their potential impact on global health and highlighting the need for proactive strategies to address emerging challenges.
I. The Rise of Chronic Diseases: A Growing Global Burden
The world is witnessing a dramatic shift in the disease burden, with chronic conditions like heart disease, cancer, diabetes, and respiratory illnesses increasingly dominating the health landscape. This trend is driven by multiple factors, including:
- Aging populations: As life expectancy increases, the prevalence of age-related chronic diseases rises.
- Lifestyle changes: Sedentary lifestyles, unhealthy diets, and increased tobacco and alcohol consumption contribute to chronic disease development.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to air pollution, climate change, and environmental toxins can exacerbate existing chronic conditions.
II. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Looming Threat
The emergence and spread of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) pose a significant threat to global health. This phenomenon occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites develop resistance to antimicrobial drugs, making infections harder to treat and potentially leading to life-threatening complications.
- Overuse and misuse of antibiotics: Inappropriate prescription and overuse of antibiotics in both human and animal healthcare drive the selection and spread of resistant strains.
- Lack of investment in new antibiotics: The development of new antimicrobial drugs is hindered by high costs and limited financial returns.
- Global interconnectedness: Travel and trade facilitate the rapid spread of resistant organisms across borders.
III. Emerging and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases: A Constant Challenge
The world remains vulnerable to emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases, driven by factors such as:
- Climate change: Changing environmental conditions can create favorable environments for disease vectors, such as mosquitoes, and facilitate the spread of pathogens.
- Globalization: Increased travel and trade can accelerate the transmission of infectious agents across borders.
- Antimicrobial resistance: The emergence of drug-resistant strains of pathogens increases the difficulty of treating infections.
IV. Mental Health: A Growing Concern
Mental health disorders are increasingly recognized as a significant public health issue, with rising prevalence rates worldwide. Factors contributing to this trend include:
- Social isolation and loneliness: Modern lifestyles characterized by increased digital connectivity and reduced social interaction can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness, contributing to mental health issues.
- Stress and anxiety: Rapid societal changes, economic pressures, and constant information overload contribute to increased stress and anxiety levels.
- Stigma and discrimination: Social stigma and discrimination surrounding mental health issues can deter individuals from seeking help.
V. The Impact of Technology on Epidemiology
Technological advancements are transforming the field of epidemiology, offering new tools and approaches for studying disease patterns and developing interventions:
- Big data analytics: The collection and analysis of large datasets, including electronic health records, social media data, and environmental data, provide valuable insights into disease trends and risk factors.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): AI algorithms can be used to predict disease outbreaks, identify potential risk factors, and develop personalized interventions.
- Telemedicine and remote monitoring: These technologies facilitate remote healthcare delivery and enable the monitoring of patients with chronic conditions, improving access to care and reducing healthcare costs.
VI. The Importance of Public Health Infrastructure
Effective public health infrastructure is crucial for addressing the challenges posed by secular trends in epidemiology. This infrastructure includes:
- Surveillance systems: Robust surveillance systems are essential for monitoring disease trends, identifying outbreaks, and evaluating the effectiveness of public health interventions.
- Laboratory capacity: Adequate laboratory capacity is needed for accurate diagnosis and monitoring of disease outbreaks.
- Health workforce: A well-trained and adequately resourced health workforce is essential for delivering public health services.
VII. The Role of Global Collaboration
Addressing secular trends in epidemiology requires global collaboration and coordination:
- Sharing of data and best practices: International collaboration facilitates the exchange of data, research findings, and best practices for tackling global health challenges.
- Joint research initiatives: Collaborative research efforts are essential for developing new diagnostics, treatments, and prevention strategies for emerging and re-emerging diseases.
- Financial support: International funding mechanisms are needed to support research, capacity building, and the development of public health programs in low- and middle-income countries.
VIII. The Need for a Multi-Sectoral Approach
Addressing secular trends in epidemiology necessitates a multi-sectoral approach, involving collaboration between:
- Health ministries: Health ministries play a crucial role in developing and implementing public health policies and programs.
- Research institutions: Research institutions are responsible for conducting epidemiological research, identifying risk factors, and developing new interventions.
- Community organizations: Community organizations play a vital role in educating the public, promoting healthy behaviors, and providing support services.
- Private sector: The private sector can contribute to public health by developing new technologies, providing access to healthcare, and promoting healthy lifestyles.
Related Searches:
- Epidemiology Trends: This search explores current and emerging trends in epidemiology, providing insights into the evolving health landscape.
- Chronic Disease Trends: This search focuses on the rising prevalence of chronic diseases and their impact on global health, highlighting factors contributing to their emergence.
- Antimicrobial Resistance Trends: This search examines the growing threat of antimicrobial resistance, exploring the drivers of resistance and potential solutions.
- Emerging Infectious Diseases: This search focuses on the emergence of new infectious diseases and their potential impact on public health, highlighting factors contributing to their emergence and spread.
- Mental Health Trends: This search explores the increasing prevalence of mental health disorders and their impact on individuals, families, and society, highlighting factors contributing to this trend.
- Technology in Epidemiology: This search examines the role of technology in epidemiology, highlighting how technological advancements are transforming the field.
- Public Health Infrastructure: This search explores the importance of strong public health infrastructure for addressing health challenges, highlighting key components of effective infrastructure.
- Global Health Collaboration: This search examines the importance of international collaboration in addressing global health challenges, highlighting the benefits of shared data, research, and resources.
FAQs:
Q: What are some key factors driving secular trends in epidemiology?
A: Key factors driving secular trends include aging populations, lifestyle changes, environmental factors, globalization, technological advancements, and antimicrobial resistance.
Q: How can technology be used to address secular trends in epidemiology?
A: Technology can be used for data collection and analysis, disease surveillance, early detection and diagnosis, and development of personalized interventions.
Q: What is the role of public health infrastructure in addressing secular trends?
A: Public health infrastructure plays a crucial role in monitoring disease trends, identifying outbreaks, and delivering effective public health interventions.
Q: Why is global collaboration essential for addressing secular trends?
A: Global collaboration is essential for sharing data, best practices, and resources to address global health challenges effectively.
Q: What are some examples of multi-sectoral approaches to address secular trends?
A: Multi-sectoral approaches involve collaboration between health ministries, research institutions, community organizations, and the private sector.
Tips:
- Stay informed about emerging trends: Continuously monitor research findings and public health reports to stay updated on the latest developments in epidemiology.
- Promote healthy lifestyles: Encourage healthy behaviors, such as regular exercise, balanced diets, and avoiding tobacco use, to reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Support public health initiatives: Advocate for increased investment in public health infrastructure, research, and programs.
- Be aware of antimicrobial resistance: Use antibiotics only when necessary and complete the full course of treatment as prescribed.
- Promote mental health awareness: Reduce stigma surrounding mental health issues and encourage individuals to seek help when needed.
Conclusion:
Secular trends in epidemiology are shaping the future of public health, posing both challenges and opportunities. Understanding these trends, anticipating their impact, and developing proactive strategies are essential for ensuring a healthier future for all. By investing in public health infrastructure, promoting healthy lifestyles, fostering global collaboration, and embracing technological advancements, we can effectively address the challenges posed by these trends and create a world where everyone can live longer, healthier lives.




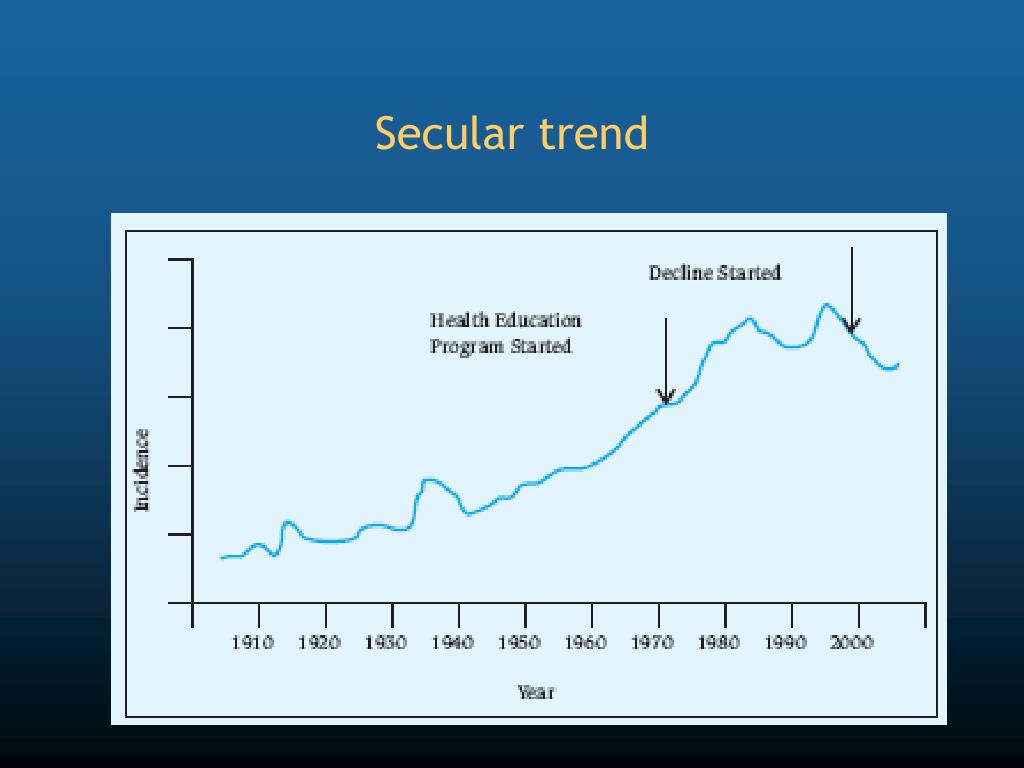
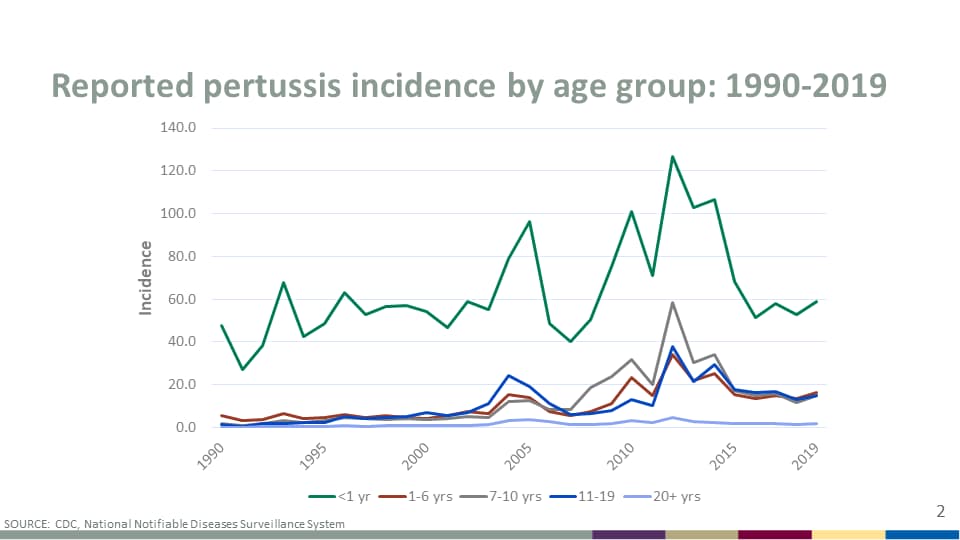
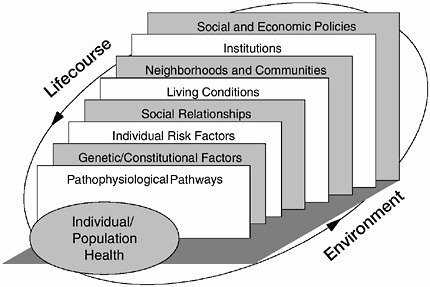
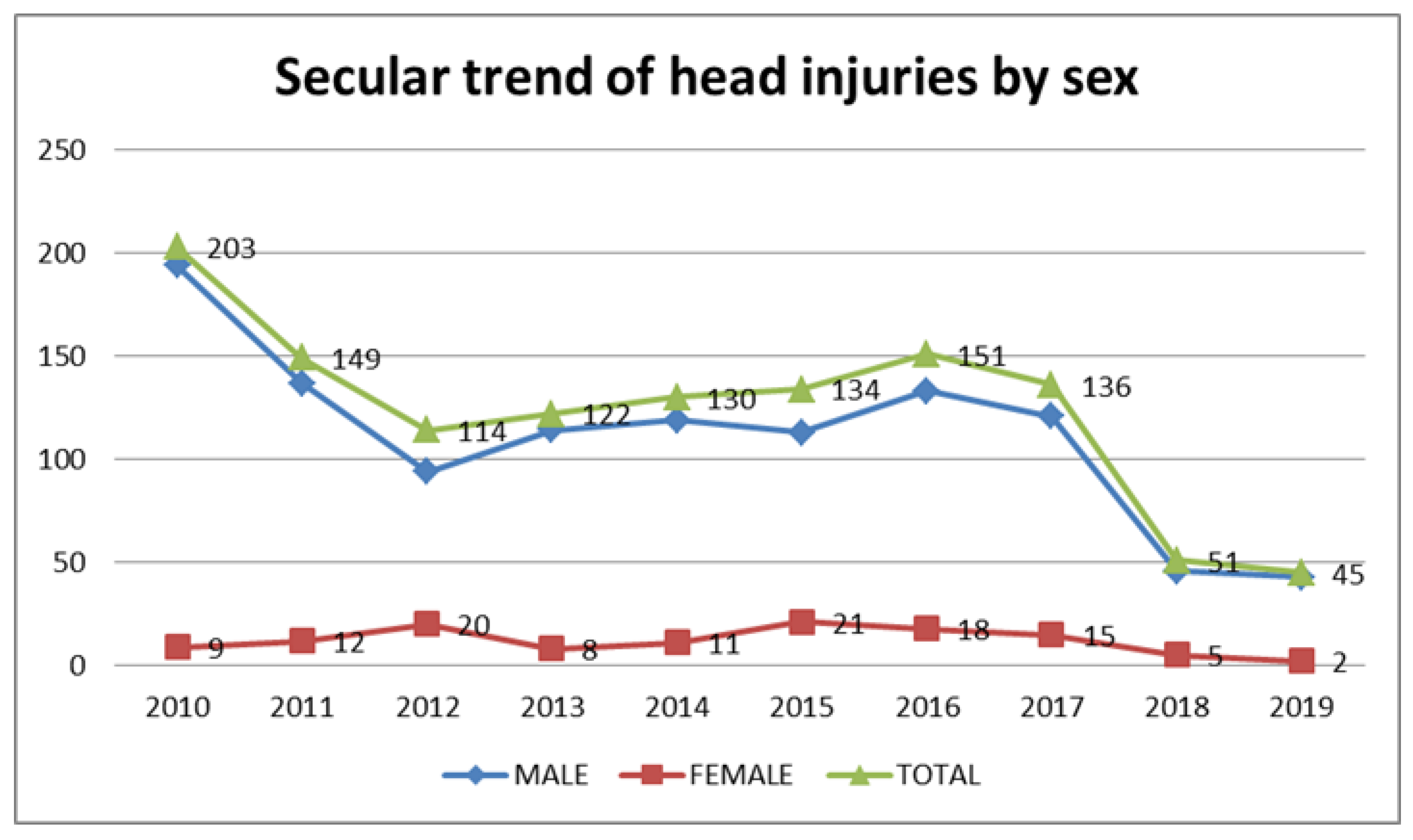
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Secular Trends in Epidemiology 2025: Shaping the Future of Public Health. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!