Shaping the Future of Production: Industrial Manufacturing Trends in 2025
Related Articles: Shaping the Future of Production: Industrial Manufacturing Trends in 2025
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Shaping the Future of Production: Industrial Manufacturing Trends in 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Shaping the Future of Production: Industrial Manufacturing Trends in 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Shaping the Future of Production: Industrial Manufacturing Trends in 2025
- 3.1 1. The Rise of Automation and Robotics
- 3.2 2. The Power of Data and Analytics
- 3.3 3. The Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 3.4 4. The Rise of Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
- 3.5 5. The Importance of Sustainability and Circular Economy
- 3.6 6. The Power of the Internet of Things (IoT)
- 3.7 7. The Rise of Cloud Computing and Digital Twins
- 3.8 8. The Importance of Cybersecurity
- 3.9 Related Searches:
- 3.10 FAQs about Industrial Manufacturing Trends 2025:
- 3.11 Tips for Manufacturers Adapting to Industrial Manufacturing Trends 2025:
- 3.12 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Shaping the Future of Production: Industrial Manufacturing Trends in 2025
The industrial manufacturing landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer demands, and a growing emphasis on sustainability. As we approach 2025, several key trends are poised to reshape the industry, creating new opportunities and challenges for manufacturers worldwide. Understanding these trends is crucial for businesses seeking to remain competitive and thrive in the evolving manufacturing ecosystem.
Industrial Manufacturing Trends 2025 are not just about technological innovations; they represent a fundamental shift in how products are designed, manufactured, and delivered. These trends are characterized by an increased focus on automation, data-driven decision making, and a commitment to sustainable practices.
1. The Rise of Automation and Robotics
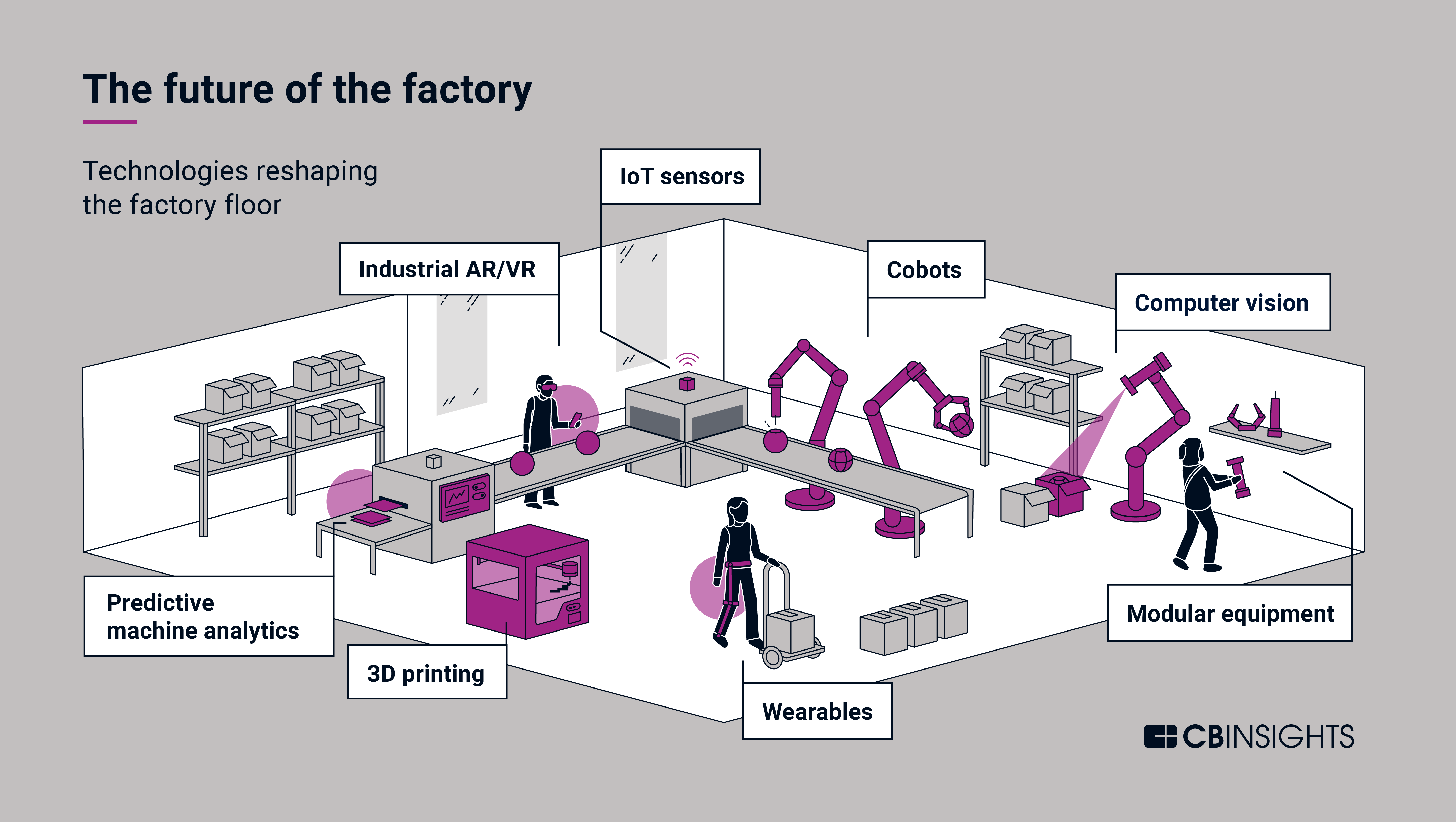
Automation and robotics are rapidly changing the face of manufacturing. The adoption of industrial robots, collaborative robots (cobots), and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) is increasing, driven by the need to enhance productivity, improve efficiency, and address labor shortages.
- Industrial Robots: These powerful machines are increasingly used for tasks like welding, painting, assembly, and material handling. They offer higher precision, faster production rates, and the ability to operate in hazardous environments.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Designed to work alongside humans, cobots offer flexibility and adaptability, enabling them to perform tasks that require human interaction and judgment.
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): AGVs are autonomous vehicles that transport materials within factories and warehouses, minimizing manual labor and improving logistics efficiency.
The benefits of automation extend beyond increased productivity. It also helps manufacturers:
- Improve product quality: Robots and automated systems offer greater precision and consistency, leading to fewer defects and higher product quality.
- Enhance safety: Automation can reduce the risk of workplace accidents by handling dangerous or repetitive tasks.
- Boost flexibility: Automation enables manufacturers to respond quickly to changing market demands and customize production lines.
2. The Power of Data and Analytics
Data is becoming the lifeblood of modern manufacturing. Manufacturers are increasingly leveraging data analytics to optimize processes, improve decision-making, and gain a competitive edge.
- Predictive Maintenance: Using data from sensors and equipment, manufacturers can predict potential failures and schedule maintenance proactively, minimizing downtime and production losses.
- Real-time Monitoring and Control: Data analytics enables real-time monitoring of production processes, allowing for immediate adjustments and optimization based on performance metrics.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Data analysis helps manufacturers optimize their supply chains, improving efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring timely delivery of materials.
By harnessing the power of data, manufacturers can:
- Improve operational efficiency: Identify bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and streamline production processes.
- Enhance product quality: Analyze data to identify and address quality issues proactively, leading to higher product quality and customer satisfaction.
- Gain deeper insights: Understand customer preferences, market trends, and competitor activities, informing strategic decisions.
3. The Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is rapidly transforming the manufacturing industry, bringing new capabilities for automation, optimization, and predictive analysis.
- AI-powered Quality Control: AI algorithms can analyze images and data to detect defects and inconsistencies in real-time, ensuring product quality and reducing human error.
- AI-driven Process Optimization: AI can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and optimize production processes, maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste.
- AI-powered Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms can analyze sensor data to predict equipment failures with greater accuracy, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
AI offers manufacturers significant advantages:
- Increased productivity: AI-powered automation and optimization can significantly enhance productivity and reduce labor costs.
- Improved efficiency: AI algorithms can identify and eliminate inefficiencies in production processes, leading to greater resource utilization.
- Enhanced decision-making: AI provides valuable insights and data-driven recommendations, supporting better informed decisions.
4. The Rise of Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is rapidly gaining traction in the manufacturing industry, offering new possibilities for product design, prototyping, and production.
- Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing enables manufacturers to quickly create prototypes and test different designs, accelerating product development cycles.
- Customizable Production: 3D printing allows for the production of highly customized products, meeting specific customer needs and enabling mass personalization.
- On-demand Manufacturing: 3D printing enables manufacturers to produce parts and products on demand, reducing inventory costs and lead times.
3D printing offers several benefits for manufacturers:
- Reduced lead times: 3D printing eliminates the need for traditional tooling and allows for faster production cycles.
- Increased flexibility: 3D printing enables the production of complex geometries and customized designs, offering greater design freedom.
- Reduced waste: 3D printing minimizes material waste by producing only what is needed, promoting sustainable manufacturing practices.
5. The Importance of Sustainability and Circular Economy
Sustainability is no longer a niche concern; it’s becoming a core value for manufacturers. Consumers are increasingly demanding sustainable products and processes, and businesses are responding by adopting eco-friendly practices.
- Energy Efficiency: Manufacturers are investing in energy-efficient technologies and processes to reduce their carbon footprint and operating costs.
- Waste Reduction and Recycling: Manufacturers are implementing strategies to minimize waste, recycle materials, and adopt circular economy principles.
- Sustainable Materials: Manufacturers are sourcing and using sustainable materials like recycled plastics, bio-based materials, and renewable resources.
Sustainability initiatives offer manufacturers several benefits:
- Reduced environmental impact: Sustainable practices contribute to a healthier planet and reduce the industry’s carbon footprint.
- Cost savings: Energy efficiency and waste reduction measures can lead to significant cost savings in the long run.
- Enhanced brand image: Consumers are increasingly drawn to companies with strong sustainability commitments, enhancing brand reputation.
6. The Power of the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming manufacturing by connecting devices, machines, and systems, enabling data collection, real-time monitoring, and remote control.
- Connected Factories: IoT sensors and devices collect data on production processes, equipment performance, and environmental conditions, providing real-time insights.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: IoT enables remote monitoring and control of production processes, allowing for proactive maintenance and optimization.
- Smart Supply Chains: IoT can optimize supply chains by tracking inventory levels, managing logistics, and improving communication between stakeholders.
IoT offers manufacturers several advantages:
- Improved efficiency: Real-time data and insights enable manufacturers to optimize production processes and minimize downtime.
- Enhanced visibility: IoT provides a comprehensive view of the entire manufacturing process, allowing for better decision-making.
- Increased productivity: IoT-enabled automation and optimization can significantly enhance productivity and reduce labor costs.
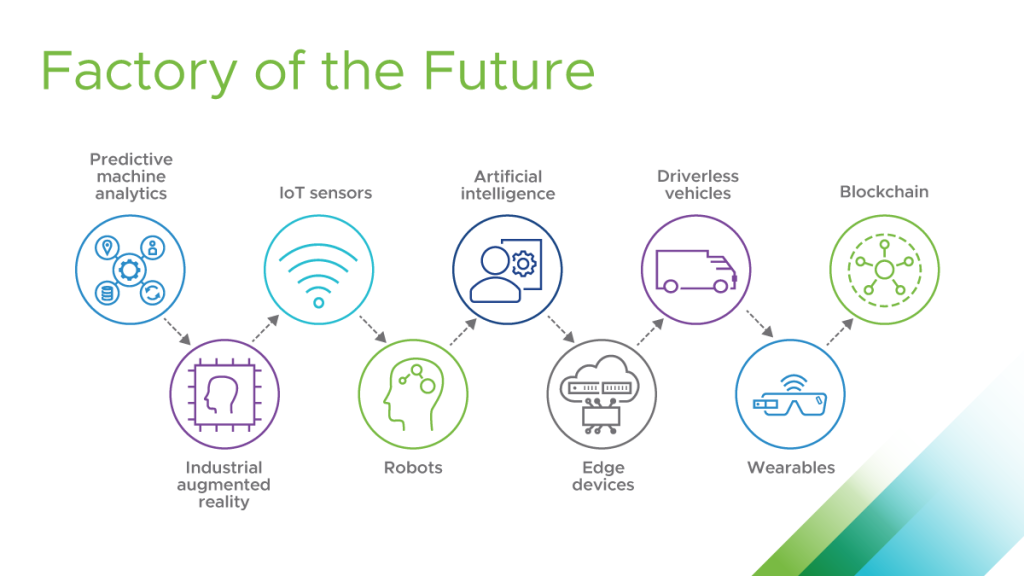
7. The Rise of Cloud Computing and Digital Twins
Cloud computing and digital twins are revolutionizing how manufacturers design, manufacture, and manage their operations.
- Cloud-based Manufacturing: Cloud computing provides a scalable and flexible infrastructure for managing data, applications, and services, enabling manufacturers to access computing resources on demand.
- Digital Twins: Digital twins are virtual representations of physical assets, providing real-time insights into their performance, health, and operation.
Cloud computing and digital twins offer manufacturers several benefits:
- Improved collaboration: Cloud-based platforms facilitate collaboration between teams, suppliers, and customers, enhancing communication and data sharing.
- Enhanced agility: Cloud computing and digital twins enable manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing market demands and adopt new technologies.
- Reduced costs: Cloud computing can lower IT infrastructure costs and streamline operations, while digital twins can optimize resource allocation and reduce maintenance costs.
8. The Importance of Cybersecurity
As manufacturing becomes increasingly digitalized, cybersecurity is becoming a critical concern. Manufacturers must protect their systems and data from cyberattacks, ensuring the integrity and reliability of their operations.
- Data Protection: Manufacturers must implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data, including customer information, production data, and intellectual property.
- Network Security: Manufacturers must secure their networks from unauthorized access and cyberattacks, protecting their systems and devices.
- Employee Training: Manufacturers must train employees on cybersecurity best practices, ensuring they are aware of potential threats and how to protect themselves.
Cybersecurity is essential for manufacturers to:
- Protect their intellectual property: Secure sensitive data from theft and unauthorized access.
- Maintain operational continuity: Prevent cyberattacks from disrupting production processes and causing downtime.
- Ensure customer trust: Protect customer data and maintain their trust in the company’s security practices.
Related Searches:
Industrial Manufacturing Trends 2025 is a broad topic, and several related searches provide more specific insights into the future of manufacturing. Here are some relevant areas to explore:
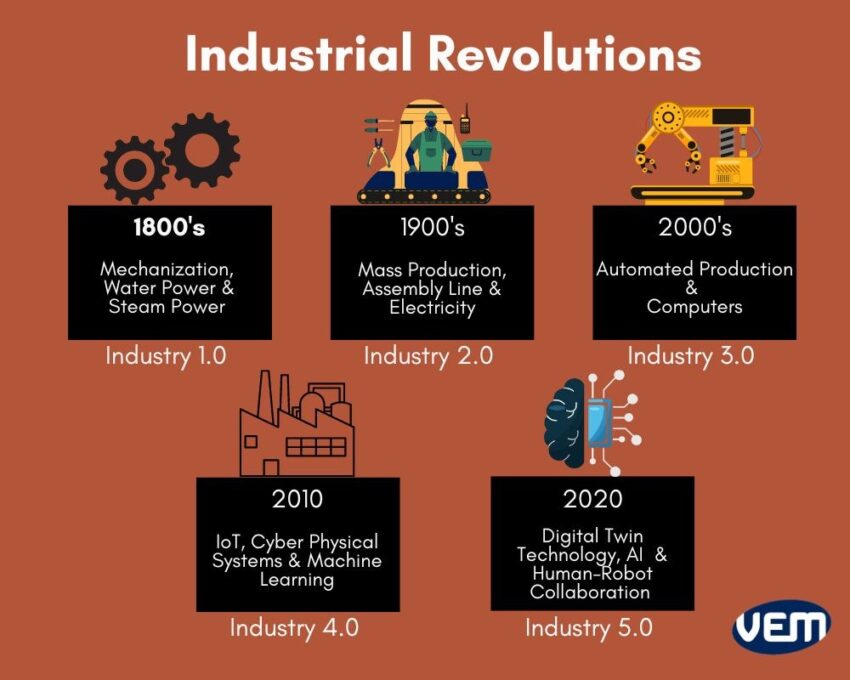
- Industry 4.0: This term refers to the fourth industrial revolution, characterized by the convergence of technologies like AI, IoT, and cloud computing. Understanding Industry 4.0 trends is crucial for manufacturers seeking to embrace digital transformation.
- Smart Factories: Smart factories leverage data and analytics to optimize production processes, improve efficiency, and enhance decision-making. Exploring smart factory concepts can help manufacturers understand how to leverage technology for greater productivity.
- Advanced Manufacturing Technologies: This includes technologies like 3D printing, robotics, and automation, which are transforming the way products are designed, manufactured, and delivered. Understanding these technologies is essential for staying ahead of the curve in the evolving manufacturing landscape.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: This encompasses environmentally friendly practices, such as energy efficiency, waste reduction, and the use of sustainable materials. Understanding sustainable manufacturing principles is crucial for manufacturers seeking to reduce their environmental impact and meet growing consumer demand for ethical products.
- Digital Transformation in Manufacturing: This involves leveraging digital technologies to enhance processes, improve decision-making, and create new business models. Exploring digital transformation strategies can help manufacturers understand how to embrace technology for greater efficiency and competitiveness.
- Future of Work in Manufacturing: This explores the impact of automation, AI, and other technologies on the workforce, highlighting the need for upskilling and reskilling to prepare for the future of work in manufacturing.
- Manufacturing Trends in Specific Industries: Exploring trends specific to industries like automotive, aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods can provide valuable insights into the unique challenges and opportunities facing each sector.
- Global Manufacturing Trends: Understanding global trends in manufacturing can help manufacturers understand the evolving competitive landscape, identify emerging markets, and adapt to changing geopolitical dynamics.
FAQs about Industrial Manufacturing Trends 2025:
1. What is the impact of automation and robotics on the manufacturing workforce?
Automation and robotics are transforming the manufacturing workforce, leading to job displacement in some areas while creating new opportunities in others. While some jobs may be automated, the demand for skilled workers who can operate, maintain, and program robots is growing. Manufacturers need to invest in training and upskilling their workforce to adapt to the changing skill requirements.
2. How can manufacturers leverage data analytics to improve their operations?
Data analytics can be used to optimize various aspects of manufacturing, from production planning and scheduling to quality control and supply chain management. Manufacturers can collect data from sensors, machines, and other sources to identify patterns, predict trends, and make data-driven decisions.
3. What are the challenges of implementing AI in manufacturing?
Implementing AI in manufacturing can be challenging, requiring investments in data infrastructure, skilled personnel, and robust cybersecurity measures. Manufacturers need to carefully evaluate the potential benefits and risks of AI before implementing it.
4. What are the benefits of 3D printing for manufacturers?
3D printing offers several benefits for manufacturers, including faster prototyping, customized production, on-demand manufacturing, and reduced waste. However, 3D printing is not suitable for all applications, and manufacturers need to carefully evaluate its suitability for their specific needs.
5. How can manufacturers embrace sustainability in their operations?
Manufacturers can embrace sustainability by implementing energy-efficient technologies, reducing waste, recycling materials, and using sustainable materials. They can also partner with suppliers who share their commitment to sustainability.
6. What are the key cybersecurity concerns for manufacturers?
Manufacturers need to be aware of the risks of cyberattacks, which can disrupt operations, compromise sensitive data, and damage their reputation. They must implement robust cybersecurity measures, including data protection, network security, and employee training.
7. How can manufacturers prepare for the future of work in manufacturing?
Manufacturers need to invest in upskilling and reskilling their workforce to prepare for the changing demands of the future. This includes training employees on new technologies, such as automation, AI, and data analytics.
8. What are the key trends shaping the future of manufacturing in specific industries?
Specific industries are facing unique challenges and opportunities as they adapt to the evolving manufacturing landscape. For example, the automotive industry is embracing electric vehicles and autonomous driving technologies, while the pharmaceutical industry is focusing on personalized medicine and advanced drug delivery systems.
Tips for Manufacturers Adapting to Industrial Manufacturing Trends 2025:
- Embrace Digital Transformation: Invest in technologies like AI, IoT, and cloud computing to enhance operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge.
- Focus on Data and Analytics: Leverage data to gain insights into production processes, customer preferences, and market trends.
- Develop a Sustainable Strategy: Implement eco-friendly practices to reduce environmental impact, meet consumer demand, and enhance brand reputation.
- Invest in Workforce Development: Train and upskill employees to adapt to the changing skill requirements of the future of work in manufacturing.
- Embrace Collaboration and Partnerships: Collaborate with suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders to leverage expertise and create new value.
- Stay Informed of Emerging Technologies: Continuously monitor emerging technologies and evaluate their potential impact on your business.
- Prioritize Cybersecurity: Implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect your data, systems, and operations from cyberattacks.
Conclusion:
Industrial Manufacturing Trends 2025 are shaping a future of production characterized by automation, data-driven decision-making, and a commitment to sustainability. Manufacturers who embrace these trends will be well-positioned to thrive in the evolving manufacturing landscape. By investing in technology, developing a skilled workforce, and adopting sustainable practices, manufacturers can unlock new opportunities, enhance efficiency, and create a more resilient and competitive industry.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shaping the Future of Production: Industrial Manufacturing Trends in 2025. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
