The Evolving Landscape of Analytics: Trends Shaping 2025
Related Articles: The Evolving Landscape of Analytics: Trends Shaping 2025
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Evolving Landscape of Analytics: Trends Shaping 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Evolving Landscape of Analytics: Trends Shaping 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Evolving Landscape of Analytics: Trends Shaping 2025
- 3.1 1. The Rise of Explainable AI (XAI)
- 3.2 2. The Power of Predictive Analytics
- 3.3 3. The Integration of Data from Multiple Sources
- 3.4 4. The Rise of Real-Time Analytics
- 3.5 5. The Importance of Data Security and Privacy
- 3.6 6. The Democratization of Analytics
- 3.7 7. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 3.8 8. The Importance of Data Governance
- 3.9 Related Searches
- 3.10 FAQs
- 3.11 Tips for Success in Analytics
- 3.12 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Evolving Landscape of Analytics: Trends Shaping 2025

The field of analytics is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing business needs, and the ever-growing volume of data. As we approach 2025, a new wave of trends is emerging, poised to reshape the way organizations collect, analyze, and utilize data for strategic decision-making. This article delves into the key trends shaping the future of analytics, exploring their implications and highlighting the opportunities they present.
1. The Rise of Explainable AI (XAI)
The increasing complexity of machine learning models has led to a growing concern about their "black box" nature. Explainable AI (XAI) addresses this challenge by providing transparency into how AI models arrive at their conclusions. XAI techniques help users understand the logic behind AI decisions, enabling them to trust the results and build confidence in their applications.
Implications:
- Increased Trust and Transparency: XAI fosters trust in AI systems by making their decision-making processes understandable and interpretable. This is crucial for industries where explainability is paramount, such as healthcare and finance.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By understanding the rationale behind AI predictions, users can make more informed and confident decisions, leading to better outcomes.
- Improved Model Development: XAI techniques can help identify and mitigate biases within AI models, leading to fairer and more accurate predictions.
Examples:
- Healthcare: XAI can help doctors understand why an AI model recommends a specific treatment plan, enabling them to make informed clinical decisions.
- Finance: XAI can provide insights into the factors influencing credit risk assessments, allowing financial institutions to make more accurate lending decisions.
2. The Power of Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics leverages historical data and statistical techniques to forecast future trends and outcomes. As data becomes more readily available and sophisticated algorithms are developed, predictive analytics is becoming increasingly powerful, enabling organizations to anticipate and capitalize on opportunities.
Implications:
- Proactive Decision-Making: Predictive analytics allows organizations to anticipate future events and take proactive measures to optimize outcomes.
- Improved Resource Allocation: By forecasting demand, organizations can allocate resources more efficiently, minimizing waste and maximizing productivity.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Predictive analytics can personalize customer interactions, offering relevant recommendations and tailored experiences.
Examples:
- Retail: Predictive analytics can forecast product demand, enabling retailers to optimize inventory levels and prevent stockouts.
- Marketing: Predictive analytics can identify potential customers and tailor marketing campaigns to maximize conversion rates.
3. The Integration of Data from Multiple Sources
The data landscape is increasingly fragmented, with data residing in various silos across different departments and systems. Integrating data from these disparate sources is crucial for gaining a holistic view of the business and unlocking its full potential.
Implications:
- Comprehensive Insights: Combining data from different sources provides a more complete picture of business operations, enabling organizations to identify hidden patterns and opportunities.
- Improved Data Quality: Integrating data from multiple sources can help identify and resolve inconsistencies, leading to more accurate and reliable insights.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By integrating data across departments, organizations can break down silos and make more informed decisions based on a complete understanding of the business.
Examples:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Integrating data from CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, and social media can provide a comprehensive view of customer behavior and preferences.
- Supply Chain Management: Integrating data from production, logistics, and sales systems can improve supply chain visibility and optimize inventory management.
4. The Rise of Real-Time Analytics
In today’s fast-paced world, organizations need to be able to analyze data and make decisions in real time. Real-time analytics provides the ability to process and interpret data as it is generated, enabling organizations to respond quickly to changing conditions and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Implications:
- Faster Decision-Making: Real-time analytics enables organizations to make decisions based on the most up-to-date information, leading to quicker responses and better outcomes.
- Improved Customer Experience: Real-time analytics can personalize customer interactions, providing tailored recommendations and resolving issues promptly.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Real-time analytics can identify and address operational bottlenecks in real time, improving efficiency and productivity.
Examples:
- E-commerce: Real-time analytics can track website traffic and customer behavior, enabling businesses to optimize website performance and personalize customer experiences.
- Manufacturing: Real-time analytics can monitor production processes and identify potential issues, preventing downtime and maximizing production efficiency.
5. The Importance of Data Security and Privacy
As organizations collect and analyze increasingly sensitive data, ensuring data security and privacy is paramount. Data breaches can have severe consequences, damaging reputation, eroding customer trust, and incurring significant financial losses.
Implications:
- Compliance with Regulations: Organizations must comply with data privacy regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
- Protecting Customer Trust: Maintaining data security and privacy is essential for building and maintaining customer trust, which is crucial for business success.
- Minimizing Risk: Implementing robust data security measures can help organizations minimize the risk of data breaches and their associated consequences.
Examples:
- Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data can help protect it from unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Implementing access control measures ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
- Data Masking: Masking sensitive data can prevent its disclosure while still allowing for analysis.
6. The Democratization of Analytics
Traditionally, analytics has been the domain of data scientists and analysts. However, with the advent of user-friendly tools and platforms, analytics is becoming more accessible to a wider range of users, empowering them to leverage data for decision-making.
Implications:
- Increased Data Literacy: Democratizing analytics encourages a data-driven culture within organizations, fostering greater data literacy among employees.
- Improved Decision-Making: By empowering a wider range of users to analyze data, organizations can leverage the insights of their entire workforce.
- Enhanced Innovation: Democratizing analytics can lead to more innovative uses of data, as employees from different departments can explore new ways to leverage data for their work.
Examples:
- Self-Service Analytics Tools: User-friendly analytics platforms allow users with minimal technical expertise to explore data and generate insights.
- Data Visualization Tools: Interactive dashboards and visualizations make data easier to understand and interpret, enabling users to extract insights quickly and efficiently.
7. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is rapidly transforming the field of analytics, enabling organizations to automate tasks, analyze large datasets, and gain deeper insights from their data. AI algorithms are becoming increasingly sophisticated, capable of learning from data and making predictions with greater accuracy.
Implications:
- Automated Insights: AI can automate tasks such as data cleaning, feature engineering, and model building, freeing up analysts to focus on higher-level activities.
- Enhanced Accuracy: AI algorithms can analyze large datasets and identify complex patterns that humans might miss, leading to more accurate predictions and insights.
- Personalized Experiences: AI can personalize customer interactions, providing tailored recommendations and improving customer satisfaction.
Examples:
- Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots can provide instant customer support and answer questions automatically.
- Recommendation Engines: AI algorithms can analyze customer behavior and recommend products or services that are likely to be of interest.
8. The Importance of Data Governance
As organizations collect and analyze increasing amounts of data, establishing robust data governance frameworks is crucial. Data governance ensures that data is collected, stored, and used responsibly, ethically, and in compliance with regulations.
Implications:
- Data Quality: Data governance ensures that data is accurate, consistent, and reliable, leading to more accurate and trustworthy insights.
- Data Security: Data governance helps protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and misuse.
- Compliance: Data governance ensures compliance with data privacy regulations and other relevant laws and standards.
Examples:
- Data Policies: Organizations should establish clear data policies that define how data is collected, stored, and used.
- Data Access Controls: Access control measures should be implemented to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
- Data Monitoring: Organizations should monitor data usage and security to identify and address potential issues.
Related Searches
1. Future of Analytics:
- Predictive Analytics Trends: The use of predictive analytics is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by advancements in AI and machine learning.
- Real-Time Analytics Applications: Real-time analytics is becoming increasingly important for organizations that need to make quick decisions based on the most up-to-date information.
- Data Visualization Best Practices: Data visualization is becoming increasingly important for communicating insights to a wider audience.
2. Analytics Tools and Technologies:
- Cloud-Based Analytics Platforms: Cloud-based analytics platforms offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- Data Science Tools: Data science tools are becoming more user-friendly, making it easier for organizations to leverage data for decision-making.
- Machine Learning Libraries: Machine learning libraries provide a wide range of algorithms and tools for building and deploying AI models.
3. Analytics in Different Industries:
- Analytics in Healthcare: Analytics is being used to improve patient care, optimize resource allocation, and develop new treatments.
- Analytics in Finance: Analytics is being used to detect fraud, manage risk, and make investment decisions.
- Analytics in Retail: Analytics is being used to personalize customer experiences, optimize inventory levels, and improve marketing campaigns.
4. Analytics Careers:
- Data Scientist Jobs: The demand for data scientists is expected to continue growing in the coming years.
- Data Analyst Jobs: Data analysts are in high demand to collect, analyze, and interpret data for organizations.
- Business Intelligence Analyst Jobs: Business intelligence analysts use data to help organizations make better business decisions.
5. Analytics Education:
- Data Science Courses: Universities and online platforms offer a wide range of data science courses.
- Analytics Certifications: Professional certifications can help individuals demonstrate their analytics skills and knowledge.
- Data Literacy Training: Data literacy training can help employees understand the basics of data and its importance for decision-making.
6. Analytics Case Studies:
- Real-World Applications of Analytics: Case studies showcase how organizations are using analytics to solve real-world problems and achieve business goals.
- Success Stories in Analytics: Success stories highlight the benefits of using analytics for organizations of all sizes and industries.
- Analytics Best Practices: Case studies can provide insights into best practices for implementing analytics solutions.
7. Analytics Industry Events:
- Analytics Conferences: Conferences and events provide a platform for industry professionals to network, learn, and share insights.
- Analytics Webinars: Webinars offer a convenient way to learn about the latest trends and technologies in analytics.
- Analytics Blogs and Articles: Blogs and articles provide valuable insights into the latest developments in the field of analytics.
8. Analytics Resources:
- Analytics Software Vendors: Software vendors offer a wide range of analytics tools and platforms.
- Analytics Consulting Firms: Consulting firms provide expertise in analytics strategy, implementation, and optimization.
- Analytics Communities: Online communities provide a platform for analytics professionals to connect and share knowledge.
FAQs
1. What are the key trends in analytics for 2025?
The key trends in analytics for 2025 include the rise of explainable AI (XAI), the power of predictive analytics, the integration of data from multiple sources, the rise of real-time analytics, the importance of data security and privacy, the democratization of analytics, the rise of artificial intelligence (AI), and the importance of data governance.
2. How will these trends impact businesses?
These trends will empower businesses to make more informed decisions, improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and gain a competitive advantage.
3. What are the benefits of using analytics?
The benefits of using analytics include improved decision-making, enhanced customer experiences, increased operational efficiency, and greater competitive advantage.
4. What are the challenges of implementing analytics?
The challenges of implementing analytics include data quality issues, data security concerns, a lack of skilled personnel, and resistance to change.
5. How can organizations prepare for the future of analytics?
Organizations can prepare for the future of analytics by investing in data infrastructure, developing data literacy among employees, and adopting a data-driven culture.
Tips for Success in Analytics
- Focus on Data Quality: Ensure that data is accurate, consistent, and reliable.
- Invest in Data Infrastructure: Build a robust data infrastructure to support the increasing volume and complexity of data.
- Develop Data Literacy: Foster a data-driven culture within the organization by promoting data literacy among employees.
- Embrace New Technologies: Stay up-to-date on the latest analytics technologies and tools.
- Prioritize Data Security and Privacy: Implement robust data security measures to protect sensitive data.
- Collaborate with Experts: Partner with data scientists, analysts, and other experts to leverage their knowledge and skills.
- Focus on Business Outcomes: Ensure that analytics initiatives are aligned with business goals and objectives.
Conclusion
The trends shaping the future of analytics are creating exciting opportunities for organizations to leverage data for strategic decision-making and competitive advantage. By embracing these trends and investing in the right technologies and skills, organizations can unlock the full potential of data and drive business growth in the years to come. The future of analytics is bright, promising a world where data-driven insights are essential for success in every industry.


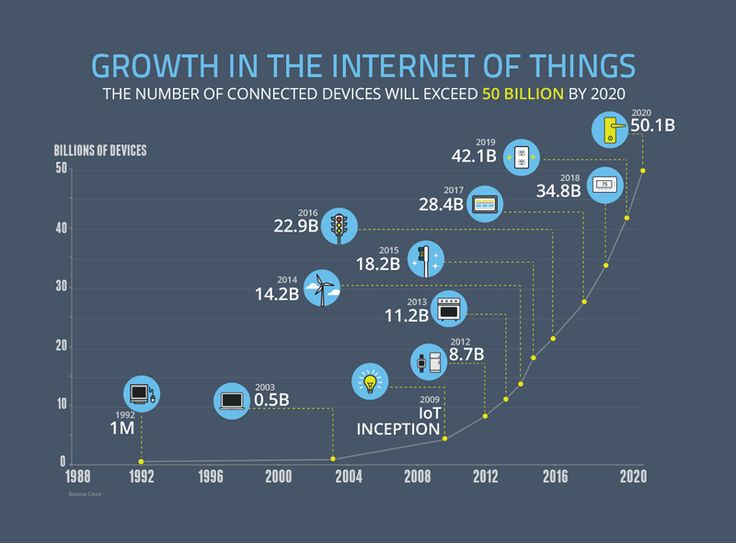
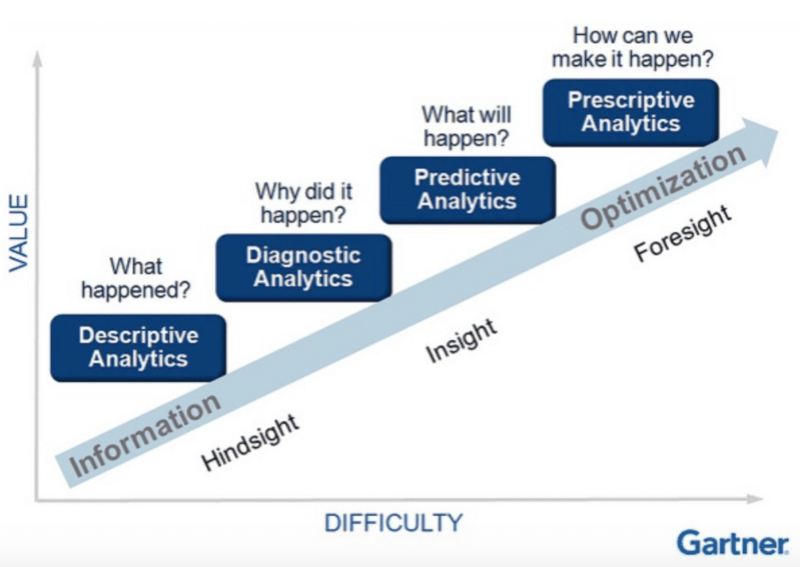


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Evolving Landscape of Analytics: Trends Shaping 2025. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!