The Future of Manufacturing: Trends Shaping the Industry in 2025
Related Articles: The Future of Manufacturing: Trends Shaping the Industry in 2025
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Future of Manufacturing: Trends Shaping the Industry in 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Future of Manufacturing: Trends Shaping the Industry in 2025

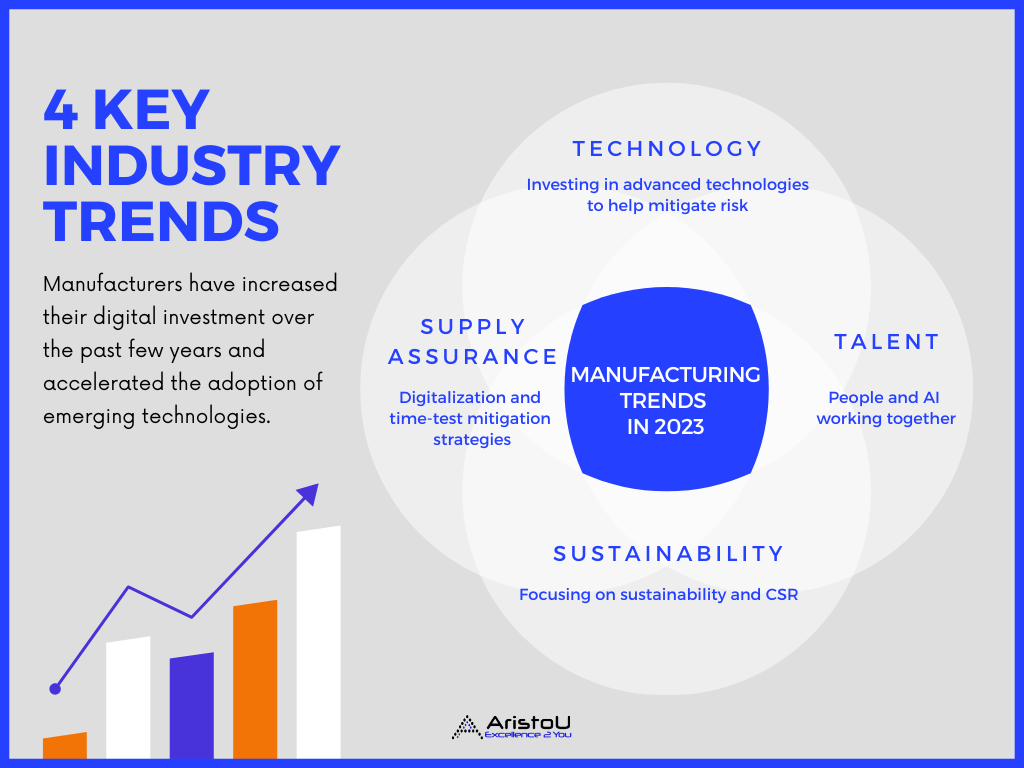
The manufacturing industry is undergoing a dramatic transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer demands, and a global shift towards sustainability. As we approach 2025, the landscape is set to be further reshaped by a confluence of trends that will redefine how products are designed, manufactured, and delivered. Understanding these trends is crucial for manufacturers to remain competitive, adapt to changing market dynamics, and secure their future success.
1. Digital Transformation and Industry 4.0
At the forefront of this evolution is the convergence of physical and digital realms, known as Industry 4.0. This paradigm shift leverages technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and advanced analytics to create intelligent, interconnected manufacturing systems.
-
Benefits:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Real-time data collection and analysis enable optimized production processes, reducing downtime, waste, and costs.
- Improved Quality Control: AI-powered systems can detect anomalies and defects, leading to higher product quality and fewer recalls.
- Greater Flexibility: Manufacturers can quickly adapt to changing customer demands and market trends, enabling agile production.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Data sharing and communication across the entire value chain foster collaboration between stakeholders, optimizing supply chains and streamlining operations.
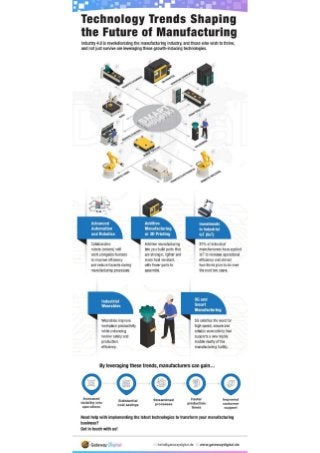
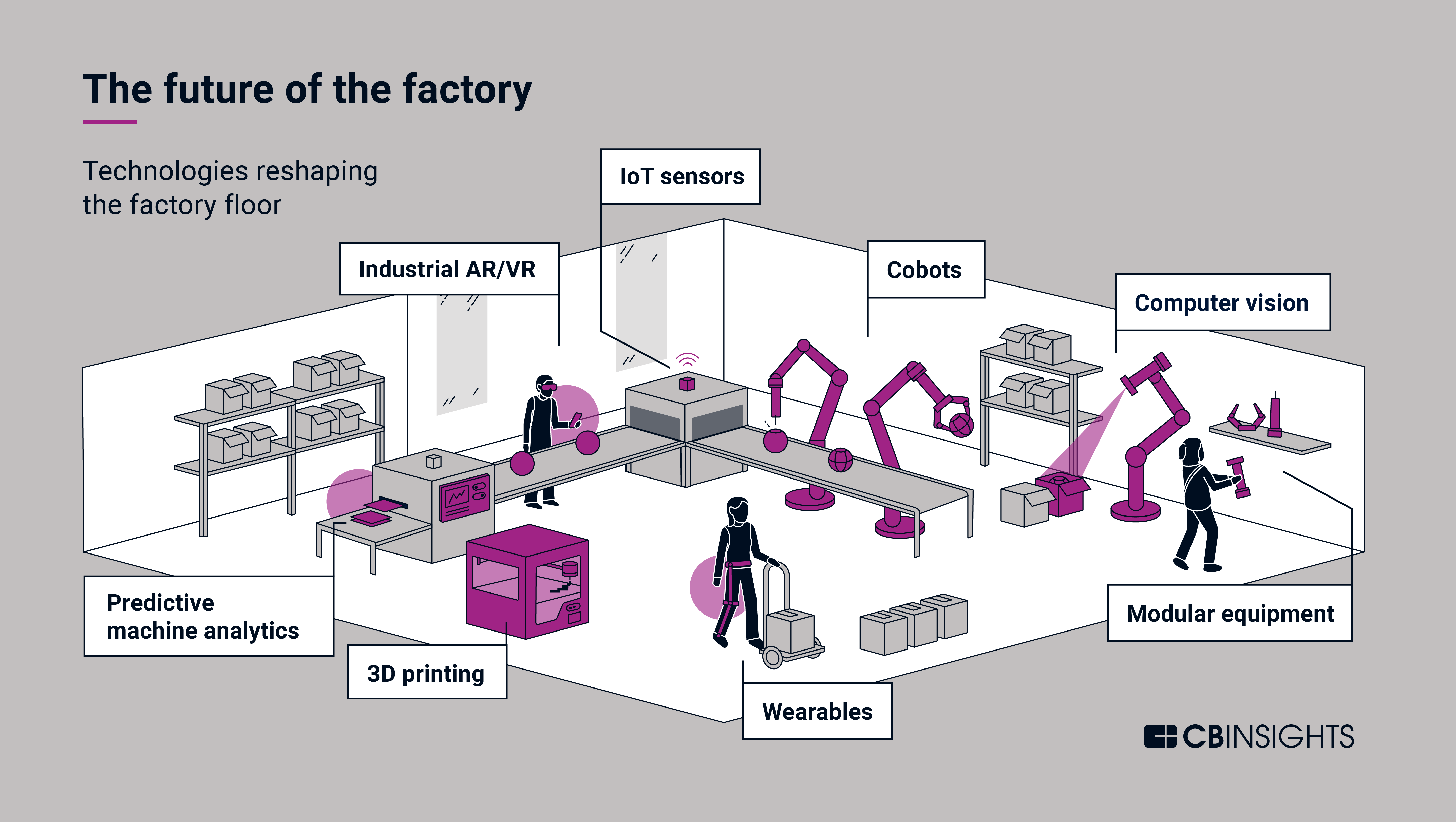
2. Advanced Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation are playing an increasingly significant role in manufacturing, handling repetitive and hazardous tasks, and improving overall efficiency.
-
Benefits:
- Increased Productivity: Robots work tirelessly and consistently, boosting production output and reducing labor costs.
- Enhanced Safety: Robots can perform dangerous tasks, protecting human workers from potential hazards.
- Improved Accuracy and Precision: Robots execute tasks with high accuracy and precision, reducing errors and improving product quality.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Robots can be easily reprogrammed and redeployed, adapting to changing production requirements and scaling operations as needed.
3. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is revolutionizing product design and production. It allows manufacturers to create complex geometries and customized products on demand, reducing lead times, minimizing waste, and enabling greater design freedom.
-
Benefits:
- Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing enables quick and cost-effective prototyping, accelerating product development cycles.
- Mass Customization: Manufacturers can personalize products based on individual customer preferences, offering unique and tailored solutions.
- On-Demand Production: 3D printing allows for localized and on-demand production, reducing transportation costs and lead times.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: 3D printing reduces material waste and enables the use of recycled materials, promoting sustainability.
4. Sustainable Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry is facing increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices, minimizing environmental impact and resource consumption.
-
Benefits:
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Sustainable manufacturing practices aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and minimize the environmental impact of production.
- Resource Conservation: Utilizing renewable energy sources, optimizing material usage, and implementing waste reduction strategies conserve valuable resources.
- Improved Brand Image: Consumers are increasingly demanding sustainable products and practices, making sustainability a key differentiator for brands.
- Cost Savings: Implementing sustainable practices can lead to long-term cost savings through reduced energy consumption, waste disposal, and material usage.
5. Data Analytics and Predictive Maintenance
Data analytics plays a crucial role in optimizing manufacturing processes. By analyzing real-time data from machines and equipment, manufacturers can identify potential issues, predict maintenance needs, and prevent costly downtime.
-
Benefits:
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing sensor data, manufacturers can predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance before breakdowns occur, preventing costly downtime and production disruptions.
- Process Optimization: Analyzing data from production processes allows manufacturers to identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and improve overall efficiency.
- Quality Improvement: Data analysis can help identify factors influencing product quality, enabling manufacturers to implement corrective measures and enhance product consistency.
- Enhanced Decision Making: Data insights provide valuable information for informed decision-making, driving continuous improvement across the manufacturing process.
6. The Rise of the Connected Workforce
The manufacturing workforce is evolving, with greater emphasis on digital skills and collaboration. Connected workers leverage technology to access information, communicate with colleagues, and collaborate remotely, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
-
Benefits:
- Enhanced Training and Development: Digital platforms enable access to online training resources, upskilling workers and improving their skillsets.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration: Digital tools facilitate seamless communication and collaboration between workers, regardless of location, fostering teamwork and knowledge sharing.
- Real-time Data Access: Workers can access real-time data and insights, enabling them to make informed decisions and optimize their tasks.
- Increased Flexibility and Agility: Connected workers can work remotely or in flexible schedules, increasing workforce flexibility and adapting to changing demands.
7. The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity
As manufacturing becomes increasingly interconnected, cybersecurity becomes paramount. Protecting sensitive data, systems, and infrastructure from cyber threats is crucial for maintaining operational integrity and ensuring business continuity.
-
Benefits:
- Data Protection: Robust cybersecurity measures safeguard sensitive data, including customer information, intellectual property, and financial records.
- System Integrity: Protecting manufacturing systems from cyberattacks ensures operational stability and prevents disruptions in production.
- Business Continuity: Strong cybersecurity safeguards against data breaches and system failures, minimizing disruptions and ensuring business continuity.
- Compliance with Regulations: Meeting industry-specific cybersecurity regulations and standards is crucial for maintaining compliance and avoiding legal penalties.
8. The Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is rapidly transforming the manufacturing industry, automating tasks, improving decision-making, and enhancing overall efficiency. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and predict outcomes, leading to more informed decisions and optimized processes.
-
Benefits:
- Automated Decision Making: AI systems can automate repetitive tasks and make data-driven decisions, freeing up human workers to focus on more complex and strategic tasks.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can analyze historical data and identify patterns to predict future outcomes, enabling manufacturers to anticipate problems and optimize production processes.
- Quality Control: AI-powered systems can detect defects and anomalies in real-time, improving product quality and reducing waste.
- Personalized Customer Experiences: AI can analyze customer data to personalize product recommendations, marketing campaigns, and customer service interactions, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Related Searches:
1. Future of Manufacturing:
- What are the future trends in manufacturing?
- How is manufacturing changing in the future?
- What will the manufacturing industry look like in 2025?
- How will technology impact manufacturing in the future?
- What are the key challenges and opportunities facing the manufacturing industry?
2. Industry 4.0:
- What is Industry 4.0 and how does it impact manufacturing?
- What are the benefits of Industry 4.0 for manufacturers?
- How can manufacturers implement Industry 4.0 solutions?
- What are the challenges of adopting Industry 4.0?
- What are the key technologies driving Industry 4.0?
3. Robotics and Automation in Manufacturing:
- How are robots changing the manufacturing industry?
- What are the benefits of using robots in manufacturing?
- What are the different types of robots used in manufacturing?
- What are the challenges of implementing robotics in manufacturing?
- How is automation impacting the future of manufacturing jobs?
4. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing):
- What is 3D printing and how is it used in manufacturing?
- What are the benefits of using 3D printing in manufacturing?
- What are the different types of 3D printing technologies?
- What are the challenges of adopting 3D printing in manufacturing?
- How is 3D printing transforming the manufacturing industry?
5. Sustainable Manufacturing:
- What is sustainable manufacturing and why is it important?
- What are the benefits of sustainable manufacturing practices?
- How can manufacturers become more sustainable?
- What are the challenges of implementing sustainable manufacturing?
- What are the key trends in sustainable manufacturing?
6. Data Analytics in Manufacturing:
- How is data analytics used in manufacturing?
- What are the benefits of using data analytics in manufacturing?
- What are the different types of data analytics used in manufacturing?
- How can manufacturers implement data analytics solutions?
- What are the challenges of using data analytics in manufacturing?
7. Cybersecurity in Manufacturing:
- Why is cybersecurity important in manufacturing?
- What are the cybersecurity threats facing the manufacturing industry?
- How can manufacturers protect themselves from cyberattacks?
- What are the best practices for cybersecurity in manufacturing?
- What are the regulations and standards for cybersecurity in manufacturing?
8. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Manufacturing:
- How is AI transforming the manufacturing industry?
- What are the benefits of using AI in manufacturing?
- What are the different types of AI used in manufacturing?
- How can manufacturers implement AI solutions?
- What are the challenges of using AI in manufacturing?
FAQs:
Q: What are the key trends shaping the manufacturing industry in 2025?
A: The manufacturing industry is being reshaped by several key trends, including Industry 4.0, advanced robotics and automation, additive manufacturing (3D printing), sustainable manufacturing, data analytics, the rise of the connected workforce, cybersecurity, and the integration of artificial intelligence (AI). These trends are driving significant changes in how products are designed, manufactured, and delivered, creating both challenges and opportunities for manufacturers.
Q: What are the benefits of Industry 4.0 for manufacturers?
A: Industry 4.0 offers numerous benefits for manufacturers, including enhanced efficiency, improved quality control, greater flexibility, and enhanced collaboration. By leveraging technologies like AI, IoT, cloud computing, and advanced analytics, manufacturers can optimize production processes, reduce waste, improve product quality, and adapt to changing market demands.
Q: How is robotics and automation impacting the manufacturing industry?
A: Robotics and automation are playing a crucial role in transforming the manufacturing industry. Robots can handle repetitive and hazardous tasks, increasing productivity, enhancing safety, improving accuracy, and providing flexibility and scalability. However, the adoption of robotics also raises concerns about job displacement and the need for workforce reskilling.
Q: What are the benefits of using 3D printing in manufacturing?
A: Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, offers numerous benefits, including rapid prototyping, mass customization, on-demand production, and sustainable manufacturing. It enables manufacturers to create complex geometries, personalize products, and reduce material waste, leading to faster product development cycles, greater design freedom, and reduced environmental impact.
Q: What are the challenges of implementing sustainable manufacturing practices?
A: Implementing sustainable manufacturing practices can be challenging, requiring significant investment in new technologies, changes in production processes, and a shift in corporate culture. However, the benefits of reduced environmental impact, resource conservation, and improved brand image outweigh the challenges, making sustainability a crucial aspect of future manufacturing.
Q: How can manufacturers implement data analytics solutions?
A: Manufacturers can implement data analytics solutions by investing in sensors, data collection systems, and software platforms. They need to establish data governance practices, ensure data quality, and develop analytics expertise within their teams. Data analytics can be used to optimize production processes, predict equipment failures, improve product quality, and make more informed decisions.
Q: What are the cybersecurity threats facing the manufacturing industry?
A: The manufacturing industry faces various cybersecurity threats, including data breaches, system failures, ransomware attacks, and industrial espionage. These threats can disrupt production, compromise sensitive data, and damage brand reputation. Manufacturers need to implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect their systems, data, and infrastructure.
Q: How is AI transforming the manufacturing industry?
A: AI is transforming the manufacturing industry by automating tasks, improving decision-making, and enhancing overall efficiency. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and predict outcomes, leading to more informed decisions, optimized processes, and enhanced product quality.
Tips for Success in the Manufacturing Industry in 2025:
- Embrace Digital Transformation: Invest in technologies like AI, IoT, and cloud computing to drive efficiency, improve quality, and enhance flexibility.
- Adopt Robotics and Automation: Automate repetitive and hazardous tasks to boost productivity, enhance safety, and improve accuracy.
- Explore Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Utilize 3D printing for rapid prototyping, mass customization, and on-demand production.
- Prioritize Sustainability: Implement sustainable manufacturing practices to reduce environmental impact, conserve resources, and enhance brand image.
- Leverage Data Analytics: Analyze real-time data to optimize production processes, predict equipment failures, and improve product quality.
- Cultivate a Connected Workforce: Invest in training and development programs to upskill workers and empower them with digital skills.
- Strengthen Cybersecurity: Implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data, systems, and infrastructure from cyberattacks.
- Integrate Artificial Intelligence (AI): Explore AI solutions to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and enhance overall efficiency.
Conclusion:
The manufacturing industry in 2025 will be characterized by a dynamic landscape shaped by technological advancements, evolving consumer demands, and a global shift towards sustainability. Manufacturers who embrace these trends, adopt innovative technologies, and adapt to changing market dynamics will be well-positioned to thrive in this evolving environment. By leveraging the power of Industry 4.0, embracing automation, adopting sustainable practices, and integrating AI, manufacturers can unlock new opportunities, enhance efficiency, and secure their future success. The future of manufacturing is bright, and those who adapt and innovate will shape the industry’s trajectory for years to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Future of Manufacturing: Trends Shaping the Industry in 2025. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!